Typical monthly costs included in the debt-to-income ratio:
- credit card payments
- student loans
- auto loan/leases
- personal loans
- alimony
- child support
- mortgage loans and home equity loans on other properties you own
- housing costs on subject property including homeowners insurance, mortgage insurance, property tax, HOA dues
All the above count against your income, so if you can eliminate or reduce these debts, your income go will further in terms of what you’re able to afford.
When it comes to plastic, the minimum credit card payment listed on your credit report will be considered. All the more reason to apply for a mortgage when all your credit cards are paid off, with no new charges, if practical.
Some banks and lenders allow installment (charge) credit cards such as those issued by American Express to be excluded from the debt-to-income ratio as they often account for thousands of dollars a month, and likely get paid off in full monthly.
How do we factor in loan-to-income ratios?
Across our bridging products, funding is secured against property – the building invested in, or an existing asset. Specialist finance can support property investors who may not have high levels of income, or who have unique income sources.
Our funding is for foreign national buyers, the self-employed, seasonal workers, or anyone else who may struggle on the high street.
However, what’s important to us, is that the properties your clients are investing in hold potential. And that there’s a clear exit strategy at hand. We’re able to work with property investors purchasing a HMO with plans to move onto long-term finance, through to fix-and-flip buyers who want to sell the asset in the short term.
If you’re concerned about the how to calculate loan-to-income ratio question and what it means for your clients, we’re here for you. We’ll answer any questions you may have within 4 hours of a query, and we’ll assign you a dedicated underwriter from day 1.
How do I calculate my debt-to-income ratio?
To estimate your DTI, you can use an online debt-to-income calculator or pencil and paper.
First, gather your bills. You will need to include any of the following payments that apply:
- Full mortgage payment (including principal, interest, taxes, insurance, and any homeowner association fees) or rent payment
- Car payment
- Student loan payment
- Personal loan payment
- Minimum required payments on all credit cards or lines of credit
- Child support or alimony payments
- Any other monthly debt obligations
Then, figure out your monthly gross household income from employment and other documented sources of income, such as self-employment. Your gross income would be your total earnings before taxes and deductions. For your household, it would include the gross income of all earners. Be sure to include all sources of income, including wages and any additional sources of income.
Your debt-to-income ratio is the total amount of all these monthly expenses divided by your gross income. (You don’t need to include your discretionary spending or things that fluctuate such as your gas bill or groceries.)
 Divide your monthly expenses by your gross income to get your debt-to-income ratio.
Divide your monthly expenses by your gross income to get your debt-to-income ratio.
For example, if your total monthly debt payments come to $2,500 and your gross monthly income is $7,000, your DTI would be 36%.
Limitations Of DTI Ratio
Even though financial institutions use the DTI to assess an individual’s credit risk and creditworthiness, it does not decipher the types of debt and the expenses needed to manage those debt obligations or payments.
For example, personal loans have higher interest rates than home-equity loans, but they are all grouped when calculating the ratio. The same applies to credit cards, where transferring a balance from a higher to a lower-interest credit card would decrease spending.
Consequently, although the percentage outcome may have decreased given the transfers, the total debt remains the same, providing a false representation of your financial health and ability to manage debts.
Because of these limitations, you would want to budget above what is considered affordable or financially sensible based on your debt-to-income and make decisions based on your actual income when considering all expenses.
Loan-to-income ratios in the current market
Actually, some banks are becoming more accommodating in how they calculate loan-to-income ratios. In recent months, we’ve seen several mainstream names raise their loan-to-income limits to 5.5x or even higher.
Some commentators believe loan-to-income ratio tweaks will become more common as lenders battle for business and court borrowers. But, given our current period of high inflation and economic instability, some fear raising borrowing limits could be dangerous.
Also, when you bear down into the details of some of these increases, limiting caveats may still apply. Take a recent example from a well known building society, which raised its maximum loan-to-income ratio to 5.5x.
Its new loan-to-income increase would only be applied to households with a gross annual income of over £75,000. However, the median annual pay for full-time employees was £33,000 for the tax year ending 5 April 2022. Therefore, several first-time buyers or small-scale investors may not be able to benefit from these kinds of increases. Nevertheless, these changes are hugely beneficial for certain parts of the market. And innovation is always welcomed.
How to Calculate Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
DTI is calculated by dividing your monthly debt payments by your monthly gross income as you can see in the following debt-to-income ratio formula:
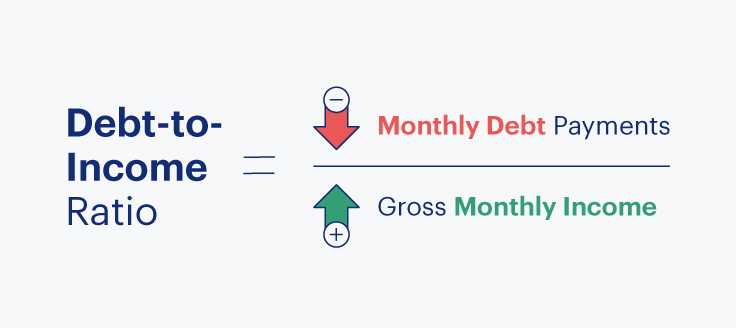
If you prefer, you can calculate your ratio by using a debt-to-income calculator, such as Bankrate’s tool.
Whether you choose to calculate your DTI ratio manually or digitally, be certain you’re working with complete data to ensure your ratio is accurate.
Monthly Debt Payments
Your total monthly debt payments cover any installment of a debt obligation. When calculating your small business debt-to-income ratio, lenders will usually review both personal and business debts.
These debt payments typically include:
- Minimum business credit-card payments
- Mortgage
- Personal and car loan installments
- Real-estate taxes
- Homeowner’s insurance
If you use your business accounts to pay off student loans, expect lenders to include those payments in your business DTI.
Monthly subscriptions and similar expenses that can be terminated at any time aren’t included in your total monthly debt payments. Variable regular expenses, such as utilities and gas, are excluded too.
Similar to your debt service coverage ratio, lenders will calculate your monthly debt payments using your existing debts and prospective loan payment.
Gross Monthly Income
Your gross monthly income is the total amount of income you earn in one month before taxes and other deductions. To estimate your gross monthly income, take your annual gross income and divide by 12.
Total Gross Monthly Income = Annual Income ÷ 12
What Is a Good Debt-to-Income Ratio?
- The lower the better
- Which is the opposite of credit scoring
- But as long as you’re below the max
- It shouldn’t affect your home loan application
Unlike a credit score, where higher is better, a good debt-to-income ratio for a mortgage is one that is low.
If you’re weighing the rent vs buy question and/or looking at properties to purchase, you should definitely know your DTI ratio well in advance to fine-tune your search.
But like credit scores, which stop benefiting you at a certain level, there’s a point where it doesn’t matter how low your DTI is either.
Really, you just want/need it to be below the key thresholds listed above. As long as you’re below those numbers, you’re “good.”
So just focus on being below the maximum ratios and you’ll have a good shot at getting approved for a mortgage, assuming you meet the other qualifying criteria for things like credit history, assets, and so forth.
As noted, it’s nice to have a buffer in case mortgage rates increase from application to funding, or if any monthly debt was left out or underestimated in error.
Tip: If your DTI is too high, you might be able to lower it by putting more money down and/or buying down your interest rate, both of which will reduce the monthly payment. So there are always options if you take a wrong turn!
Debt-to-income ratio frequently asked questions
Is 50% a good debt-to-income ratio?
Chevron iconIt indicates an expandable section or menu, or sometimes previous / next navigation options.
With a 50% debt-to-income ratio, you’ll struggle to qualify for any type of loan.
Does medical debt factor into DTI?
Chevron iconIt indicates an expandable section or menu, or sometimes previous / next navigation options.
Your medical debt does not factor into DTI calculations unless they end up on your credit report. Medical debt only shows up on your credit report if it’s more than $500, and it has fallen into debt collections.
Do utility payments factor into debt-to-income ratio calculations?
Chevron iconIt indicates an expandable section or menu, or sometimes previous / next navigation options.
No, your utility bills or phone bills do not factor into DTI calculations.
What’s the difference between debt-to-income ratio and credit score?
It’s true that a low debt-to-income ratio could help you qualify for a loan and a lower interest rate, but your credit score is also a major part of a creditor’s decision making process. While your DTI might help a creditor decide how much to lend to you, your credit score could also affect your loan terms, like the length of your loan and your annual percentage rate (APR).
The credit score really matters when you are looking to take out a new line of credit, like a loan or mortgage. Your payment history, credit utilization, and credit history all contribute to your credit score, which in turn helps creditors determine your likelihood to pay back the loan (referred to as your creditworthiness). If you have a low credit score, you may have a hard time getting a low interest rate on the loan.
Debt-to-income ratio, on the other hand, helps creditors know if they should lend to you in the first place. If they decide that it’s too high, they won’t lend to you. As a result, your debt-to-income ratio and credit score both contribute to your creditworthiness.
The Importance of DTI Ratio in Real Estate
The DTI ratio in real estate is vital because it shows your creditworthiness. Lenders want to ensure you can repay the loan and meet all your debt obligations. To determine the risk, they calculate the proportion of your monthly income that goes toward repaying debts. The higher the DTI ratio, the greater the risk of defaulting.
How lenders use DTI ratios
Lenders use DTI ratios along with your credit health, employment history, and the size of the down payment to calculate the borrowing risk. A high DTI ratio indicates that paying down the level of debt will be difficult. Therefore, borrowers with DTI ratios over 50% have very limited borrowing options.
However, there are some options to secure a loan with a high DTI. For example, you could have a cosigner on the mortgage documents. Alternatively, you could extend the loan term to lower the DTI ratio. Other options include paying off credit card debt or selling a car bought through financing.
Remember that lenders base the DTI ratio on your expenses after the loan is approved. For example, suppose you’re refinancing and consolidating debts. In that case, your qualifying DTI will reflect your expenses after the debts are consolidated.
Or say you are renting, and the new housing costs are higher than the rent price. Your qualifying DTI will be based on the new mortgage payment.
How the DTI ratio affects real estate financing
The debt-to-income ratio directly impacts your ability to secure the best real estate financing deals. You must prove to the bank, credit union, or private lender you can manage the additional debt associated with real estate investing. Even if a lender approves a loan with a high DTI, you may have to meet more stringent terms.
Here are three ways DTI ratios can affect real estate loans:
- Mortgage approvals: Getting a conventional loan with a higher DTI ratio will be difficult. Most lenders require a DTI lower than 43% before approving a mortgage application.
- Interest rates: A higher DTI could result in higher interest rates, as it implies a greater borrowing risk. Lenders typically offer the best interest rates to investors with high credit scores and low DTIs.
- Loan amount: Lenders must ensure you can meet your financial obligations. Therefore, if you have a heavy debt load, the lender may reduce the amount they are willing to lend. A larger loan amount usually requires a good-to-excellent DTI ratio.
Monthly Debt and Income Calculation Example
Suppose we’re tasked with calculating the debt to income ratio of a prospective borrower, to help determine the lending decision related to mortgage financing.
Starting off, we’ll calculate the consumer’s fixed debt payments, of which there are four.
- Mortgage Payment = $2,000
- Car Loan Payment = $600
- Student Loan Payment = $400
Thus, the total monthly debt of the consumer amounts to $3,000.
Total Monthly Debt = $2,000 + $600 + $400 =$3,000
With our first input – the total monthly debt – complete, the next step is to calculate the consumer’s gross monthly income.
In our simple example, we’ll assume that our consumer’s gross monthly income is $10,000.
Gross Monthly Income = $10,000
What Is the Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio?
When creditors determine the risk of lending you their money, they use the Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI), a metric to assess your reliability in paying them back while not accumulating more debt. The DTI is the percentage of gross monthly income spent on repaying recurring monthly debt.
Lenders like banks, credit unions, online lending platforms, and cash advances use the ratio to minimize risks when allowing people to borrow money. Usually, a lower ratio leads to lower interest rates, and higher percentages lead to higher interest rates.
Although your DTI does not directly impact your credit score, it is a part of the credit analysis process to determine someone’s trustworthiness or credit risk in repaying debt obligations when lenders decide whether or not to reject the loan or apply for credit.
In other words, it is an aspect of financial health that helps you understand your financial situation and your ability to manage current debts. For instance, Wells Fargo has its standards on determining who to lend money to, considering which range your ratio falls in.
Limitations
While DTI is useful in measuring the extent of the income that goes towards servicing debts during a month, it does not differentiate between various types of debts and the costs associated with them. This is especially relevant when credit cards carry a higher interest rate than student loans but will be grouped under debts in a DIT ratio calculation.
Similarly, if an individual were to start using a lower interest credit card from a higher interest one, their debts would automatically decline, meaning that the DTI ratio will decline too. In contrast, the total outstanding debts will not change.
Can I lower my DTI?
To change your DTI ratio, you will need to reduce your debt payments, increase your income, or do both.
For example, if you find that your DTI is too high to qualify for the loan you want, start by looking at what you spend and what you owe. Look at your net income and monthly expenses. Where can you save? Are your adult kids still on your cell phone bill? Do you have a streaming service or gym membership you’re not using? Can you make your coffee at home? You’d be surprised by how impactful paying attention and making small tweaks to your spending habits can be.
If you have higher-interest debt, you could save money by consolidating those bills into one fixed-rate personal loan with a set regular monthly payment. If you get a personal loan at a lower interest rate than you had been paying, you will reduce your overall debt load and lower your DTI.
1.
Отношение чистого долга к EBITDA — возможно, наиболее часто используемый показатель для оценки долговой нагрузки. Чистый долг — это совокупный долг компании минус денежные средства и другие ликвидные активы, которые можно быстро продать. EBITDA (от англ. Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization) — это прибыль компании до выплаты процентов по кредитам, налогов, учёта износа оборудования и амортизации.
Чистый долг/EBITDA показывает количество лет, необходимых компании для погашения своих долговых обязательств за счёт прибыли от бизнеса. Чем меньше значение этого мультипликатора, тем ниже долговая нагрузка — и тем (при прочих равных) лучше для инвестора.
К примеру, в августе 2022 года уровень соотношения чистый долг/EBITDA производителя алкогольных напитков «Белуга»составлял1,8. Комфортный уровень показателя для российского рынка, по мнению аналитиков SberCIB, не должен превышать трёх.
Избранные инструменты:
футы дюймы в сантиметрыконвертер см в футы и дюймыконвертер фунтов в кгкалькулятор жима лежаГенератор случайных цветовконвертер кг в фунтыШестнадцатеричный калькуляторкалькулятор гипотенузыКалькулятор квадратного корня (высокая точность)преобразователь температурыдвоичный калькуляторкалькулятор дисперсии (Высокая точность)случайный выборКалькулятор дня годаКалькулятор теоремы ПифагораКалькулятор модуляКалькулятор коэффициентов и процентовКалькулятор коэффициента вариацииКалькулятор числа судьбыкалькулятор комиссиигенератор случайных буквкалькулятор рентабельности продажвосьмеричный калькуляторКонвертер римских цифрКалькулятор пропорцийКалькулятор инфляции в СШАгенератор случайных строкГенератор GUID/UUIDлогарифмический калькуляторКалькулятор относительного стандартного отклонения (Высокая точность)конвертер метров в футывыбор случайного имениСписок чисел ФибоначчиКалькулятор выборки среднегоКонвертер дробей в процентахкалькулятор суммы последовательных чиселГенератор MAC-адресовКонвертер PPM в процентыкалькулятор натуральных логарифмовполучить длину строкикалькулятор золотого прямоугольникаКалькулятор чистой прибылиКалькулятор среднего арифметическогоВаш возраст (в годах, месяцах, днях, днях, часах, минутах, секундах)калькулятор золотого сеченияКалькулятор логарифмической базы 2Калькулятор стандартного отклонения выборкикалькулятор десятичной дробиКалькулятор доходности облигацийкомбинированный калькуляторКалькулятор цены за тысячу показовКалькулятор АНКконвертер дюймов в сантиметрыконвертер футов в метрыобратный тексткалькулятор сложных процентовКонвертер пси в барНепрерывный калькулятор сложных процентоврандомизатор спискаКошкам человеческие годыпобитовый калькуляторКалькулятор функции ошибкидвоичный преобразовательконвертер фунтов в граммыКалькулятор комплексных чиселдробное упрощениеНумерологический калькуляторКалькулятор одного повторного максимума (1ПМ)шестнадцатеричный преобразователь в десятичныйКалькулятор расчета заработной платыконвертер граммов в унцииДекодер азбуки МорзеCAGR калькуляторПреобразователь времени UnixКалькулятор сравнения дробейКалькулятор дополнительной функции ошибкипреобразователь двоичного кода в десятичныйHEX конвертерКонвертер процентов в PPMкалькулятор миль на галлонДвоичный в шестнадцатеричный конвертерIPv4/IPv6 в двоичный конвертерКалькулятор эквивалентной дробивосьмеричный преобразовательпреобразователь сахара в кровикалькулятор биномиального коэффициентаКалькулятор периметра эллипсаКалькулятор ПВИФА (Высокая точность)Генератор случайных английских цитаткалькулятор уклонапростой калькулятор процентовкалькулятор процентного измененияСобаки в человеческие годыкалькулятор суммы квадратоввыбор случайных чиселКонвертер унций в граммыКалькулятор процентной скидкиСортировка номеровКалькулятор отношения долга к доходу
Back-End vs. Front-End Debt-to-Income Ratios
Front-end DTI and back-end DTI are different metrics for measuring your financial health. The front-end DTI focuses solely on housing costs, while the back-end DTI ratio considers all your debts. Let’s consider these metrics in more detail.
Back-end DTI ratio
The back-end ratio calculates the level of monthly debt obligations in relation to your earnings. The calculation includes minimum payments for auto loans, credit cards, and personal loans. You should also include child support payments, if applicable. However, common household expenses—transportation, utilities, food, and entertainment—are not included.
Your back-end DTI is the figure most lenders focus on, as it provides a more comprehensive view of your monthly expenses.
A good back-end DTI ratio is typically between 33% and 36%. Although some lenders may be happy with a DTI of up to 43%, below 36% is considered good. Typically, you must meet stricter criteria when applying for a loan with a higher DTI ratio. Therefore, you should aim to lower your debt-to-income ratio as much as possible before applying for a mortgage.
The formula for the back-end DTI ratio is the same as for the standard DTI calculation. Add up your monthly debt obligations, and divide by your gross monthly income.
Front-end DTI ratio
The front-end ratio—called the housing ratio—only considers the proportion of your income that goes toward your housing payment. Housing costs include the following:
- Mortgage principal
- Investment property mortgage payments
- Interest
- Property taxes
- Homeowners insurance
- Landlord insurance
The front-end ratio is a good way to determine if you can afford the mortgage.
To calculate the DTI ratio, add up your total housing-related expenses and then divide it by your gross monthly income.
Let’s say a house buyer has an income of $7,000, and the mortgage payment will be $1,650. In that case, their front-end DTI is 23%.
Ideally, the figure for front-end DTI should be 28% or lower. A higher front-end ratio may mean higher interest rates. However, your lender may approve the loan application if you have a front-end ratio between 30% and 36% and an excellent credit score.
Зачем рассчитывать DTI
Самостоятельный расчет DTI позволяет оценить собственные возможности с экономической точки зрения. После небольших расчетов можно выяснить, какой процент от доходов составляют ваши обязательные расходы.
Проведя несложные математические действия, можно рассчитать, как лучше поступить, если возникло желание приобрести холодильник. Стоит его взять в кредит или потихоньку откладывать деньги и после накопления необходимой суммы купить холодильник без привлечения заемных средств.
ООО МКК «Киберлэндинг»
ИНН 1659182700 / ОГРН 1171690064920
420021, РФ, РТ, город Казань, улица Г. Тукая, дом 125, офис 502
Свидетельство Банка России о внесении сведений о юридическом лице в государственный реестр микрофинансовых организаций от 07.03.2018 г.
Does Your DTI Ratio Impact Your Credit?
While your DTI ratio has no direct impact on your credit score and won’t show up on your credit report, it can affect your ability to secure loans from banks and other lenders. A low DTI ratio increases the likelihood that you will be approved for the loans you apply for. That’s because lenders take a low DTI ratio as a sign that you are competent when it comes to money management and they can rely on you to pay back any debt you accrue according to the agreed-upon terms. Lenders also take a loan applicant’s DTI ratio into consideration because they want to ensure that borrowers aren’t taking out more debt than they can realistically pay back.
Although a lower DTI ratio typically makes it easier to get approved for a loan, keep in mind that it’s only one out of many factors that lenders take into consideration. When evaluating a mortgage loan application, lenders will also take a look at a potential borrower’s gross monthly income, the amount they can afford on a down payment, their credit history, and their credit score.
How to Lower Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
If looking at your debt-to-income ratio made your blood pressure rise a little, take a breath. You actually have more control over that number than you might think. If you want to lower your DTI, you need to decrease your monthly debt or increase your monthly income. Or both.
Here are a few practical tips to lower your debt-to-income ratio:
Don’t take on any more debt.
A perfect new couch that’s calling your name? That boat you’ve been eyeing for years? Nope. And nope. Taking on more debt will just make your DTI percentage rise (and also your stress level). Don’t be tempted to add any more payments to your plate. Work on getting rid of the payments you already have.
Earn additional income.
Negotiate a higher salary. Pick up a few extra hours. Start some freelance work. Anything you can do to earn more income will help lower your DTI. But don’t just earn more money for the sake of improving your debt-to-income ratio. Use that extra cash to pay off more debt.
Throw more money at your debt than just the minimum payment.
Minimum payments = minimal progress. Seriously, if you’re only paying your minimum payments, those balances will hang around forever. And nobody wants that. To pay off debt faster, start by tackling the smallest debt first, not the one with the highest interest rate (we call this the debt snowball method). When you use the debt snowball method, you’ll get quick wins and see progress on that debt right away—which will keep you motivated to pay off the rest even faster.
Get on a budget.
No, just using an amazing budgeting app (like our fave, EveryDollar) won’t make your DTI magically shrink. But what a budget will do is help you visually see where your money is going each month and track where you’re overspending. If you make adjustments to those areas, you’ll have more money to throw at your debt every single month—which will lower your DTI (and get you closer to a life without debt at all).
Рекомендации по оптимизации долговой нагрузки
Для оптимизации долговой нагрузки нужно:
правильно определить срок кредитования. Желательно, чтобы срок кредитования соответствовал сроку реализации инвестиционного проекта. Брать короткие кредиты на долгосрочный проект рискованно. Внедрение инвестиционных проектов — процесс длительный, поэтому прибыль такой проект будет приносить через несколько лет. Краткосрочные кредиты не могут быть погашены от прибыли по реализации инвестиционного проекта;
определить валюту кредита. Если бизнес зависит от изменения валютных курсов, следует быть более осторожными в управлении кредитной нагрузкой. Компании, занимающиеся импортными или экспортными операциями, находятся в постоянной зависимости от динамики курса доллара, евро или других валют. Значит, следует тщательно продумать, в какой валюте брать кредит;
соблюдать взятые обязательства по кредиту. После выдачи денег любой банк ожидает от заемщика, что он будет честным в обслуживании кредита и пунктуальным в предоставлении документов, указанных в кредитном договоре
Даже если заемщик выплачивает кредит вовремя, банку важно знать, как расходуются выделенные средства. Если деньги идут не на то, что прописано в договоре (касается инвестиционных кредитов), то могут возникнуть проблемы с банком и налоговой инспекцией
Заинтересованность в долгосрочном сотрудничестве и элементарная порядочность в конечном итоге выгодны обеим сторонам. Вероятность того, что в сложное время банк сможет пойти клиенту навстречу, будет значительно выше.
Что ещё почитать
- В 2022 году на рынках наблюдается повышенная волатильность. Как инвесторам вести себя в такой период, мы рассказывали здесь.
- EBITDA подходит не только для оценки долговой нагрузки. Что это за показатель и как его можно использовать — читайте тут.
- Всестороннее изучение компании увеличивает шансы на успешные инвестиции. О том, что ещё стоит делать инвестору, рассказываем здесь.
Не является индивидуальной инвестиционной рекомендацией. Доход от инвестирования не гарантирован. Инвестиционная деятельность сопряжена с риском неполучения ожидаемого дохода и потери части или всей суммы инвестированных средств
Банк обращает внимание Инвесторов, являющихся физическими лицами, на то, что на денежные средства, переданные Банку в рамках данных Условий, не распространяется действие Федерального закона от 23.12.2003. №177-ФЗ «О страховании вкладов в банках Российской Федерации»
Why does DTI matter?
Your DTI is important because it gives an immediate snapshot of your financial situation.
If your DTI is too high, you might struggle to cover your daily expenses, let alone save for important financial goals.
In addition, your DTI ratio can make the difference between loan approval and rejection because it’s a strong indicator of whether you can afford to add new payments to your monthly budget.
A high DTI could make it more difficult to qualify for a mortgage, car, or other kind of loan.
Many personal finance advisors believe that everyone should work to lower their DTI by eliminating most debt other than a mortgage or rent payment, and perhaps a car payment. Reducing your debt can give you more flexibility and freedom, and set you up for a rewarding future.
You could start by consolidating higher-interest debt from credit cards into a fixed-rate, fixed-term personal loan. You might be able to pay off your debt faster and save money on interest.
What Is a Good Debt-to-Income Ratio?
A good DTI depends on the loan type. Usually, the lower the debt-to-income ratio, the better your chance of securing a mortgage loan. Generally, a DTI below 50% is considered acceptable in real estate investing.
Here is a breakdown of what is considered a good DTI ratio:
- DTI below 36%: This shows you have reasonable levels of debt. You should have no problem applying for lines of credit or a new real estate loan.
- DTI 37% to 41%: You have reasonable, manageable debt levels. Lenders typically approve mortgages if you have a ratio in this range and a good credit history.
- DTI 42% to 49%: Lenders may use extra scrutiny during the loan application process to check your financial health. They could think that paying off this level of debt may be difficult. However, they will consider your whole financial picture before approving a mortgage loan.
- DTI over 50%: This indicates you have a high debt burden and may struggle to make monthly mortgage payments. Lenders typically refuse applications with DTIs over 50%.
Certain government-backed loans may allow higher DTS. Here are a few:
- FHA loans: DTI ratio of up to 57%
- USDA loans: DTI ratio of up to 41%
- VA loans: DTI of up to 60%
- Conventional loan: DTI of up to 50%
In many cases, the lender determines your risk as a borrower.
What is ideal for real estate?
Any ratio below 43% is considered good in real estate investing. However, reducing your debt-to-income ratio as much as possible makes financial sense because you can access the best mortgage products. If your DTI is between 43% and 50%, your lender may require you to have greater cash reserves to secure the real estate loan.
Что такое «Отношение долга к доходу»
Личный финансовый показатель, который измеряет отношение выплачиваемого долга заемщика к его общему доходу. Для кредиторов (в том числе ипотечных кредиторов), отношение долга к доходам (DTI) является одним из способов измерения способности человека справиться с ежемесячными платежами и погасить долги. DTI рассчитывается путем деления общей ежемесячной суммы долга на суммарный ежемесячный доход, и все это выражается в процентах. Например, Вася платит $1000 каждый месяц за ипотеку, 500$ за автомобиль в кредит и $500 за кредит на ремонт квартиры. Отсюда, общая сумма его ежемесячных выплат будет равна $2,000 ($1,000 + $500 + $500). Предположим, что ежемесячный заработок Васи составляет $6000. Его DTI будет: $2,000 ÷ $6000 = 0,33, или 33%.
Пояснение к отношению долга и дохода
Низкое соотношение долга к доходам означает хороший баланс между долгом и доходом. Наоборот, высокий показатель DTI может сигнализировать о том, что человек имеет слишком много долгов по отношению к его доходам. Согласно исследованиям ипотечных кредитов, заемщики, которые имеют более низкий показатель DTI, скорее всего, успешно справятся с ежемесячными выплатами. В США, 43% — самый высокий показатель DTI, при котором заемщик может получить положительное решение по ипотеке. При этом не более чем 28% от всей задолженности может приходиться на обслуживание ипотечного кредита.
Есть два способа снизить DTI: снизить текущую задолженность по долгу и/или увеличить ежемесячный доход. Используя вышеприведенный пример, если Вася имеет тот же ежемесячный долг в $2000, но при этом, его ежемесячный доход увеличивается до $8000, то DTI будет: $2,000 ÷ $8000 = 0,25, или 25%. Точно так же, если доход Васи остается неизменным ($ 6,000), но он досрочно погасит кредит за автомобиль и сократит свои ежемесячные повторяющиеся долговые выплаты до $1500, его DTI будет: $1500 ÷ $6000 = 0,25, или 25%.
Похожие термины
|
А-Кредит Наивысший кредитный рейтинг, который может быть присвоен заемщику кредитором. Кредиторы… |
Ипотека Ипотека — это долговой инструмент, обеспеченный залогом указанного объекта недвижимости, который… |
|
Погашение (возмещение) Погашение (возмещение) (англ. Repayment) — акт возврата денег, ранее заимствованных у кредитора… |
Залог (Обеспечение) Залог (Обеспечение) — недвижимость или другие активы, которые заемщик предлагает кредитору при… |
А-Кредит
Наивысший кредитный рейтинг, который может быть присвоен заемщику кредитором. Кредиторы…
Ипотека
Ипотека — это долговой инструмент, обеспеченный залогом указанного объекта недвижимости, который…
Погашение (возмещение)
Погашение (возмещение) (англ. Repayment) — акт возврата денег, ранее заимствованных у кредитора…
Залог (Обеспечение)
Залог (Обеспечение) — недвижимость или другие активы, которые заемщик предлагает кредитору при…
How To Calculate Your DTI Ratio
For the most part, calculating your DTI ratio is actually rather simple. First, gather information using the following steps:
-
Add up your monthly debt payments to determine your total monthly debt.
-
Determine your total monthly income before taxes.
-
Divide your total monthly debt payment by your gross monthly income.
-
If your income is higher than your debt, you will yield a decimal
-
Multiply the decimal by 100 to discover your DTI percentage.
The DTI equation is:
If you find that your debt-to-income ratio is above 50%, you might need to pay off some of your previous loans before you can consider a new purchase. While on the other hand, if your DTI ratio is below 30%, you may find that you can be approved for a larger loan than you expected.
Either way, always be aware of your most up-to-date DTI status, as the information will allow you to make more thoughtful financial decisions.
Итого ежемесячные повторяющиеся платежи по долгу
Общая ежемесячная повторяющаяся задолженность представляет собой все ваши ежемесячные повторяющиеся платежи по долговым обязательствам, таким как ссуды. Обычно они включают все регулярные платежи, которые вы не можете отменить, например платежи по ипотеке, платежи за автомобиль, платежи по студенческому кредиту, минимальные платежи по кредитной карте, платежи по личным кредитам, налоги на недвижимость и страхование домовладельцев.
Некоторые счета, такие как ежемесячные планы подписки, обычно не считаются повторяющейся задолженностью, потому что у вас есть возможность прекратить эти расходы. Кроме того, переменные регулярные расходы, такие как продукты, коммунальные услуги и газ, как правило, не включаются в ежемесячные повторяющиеся долги.





























