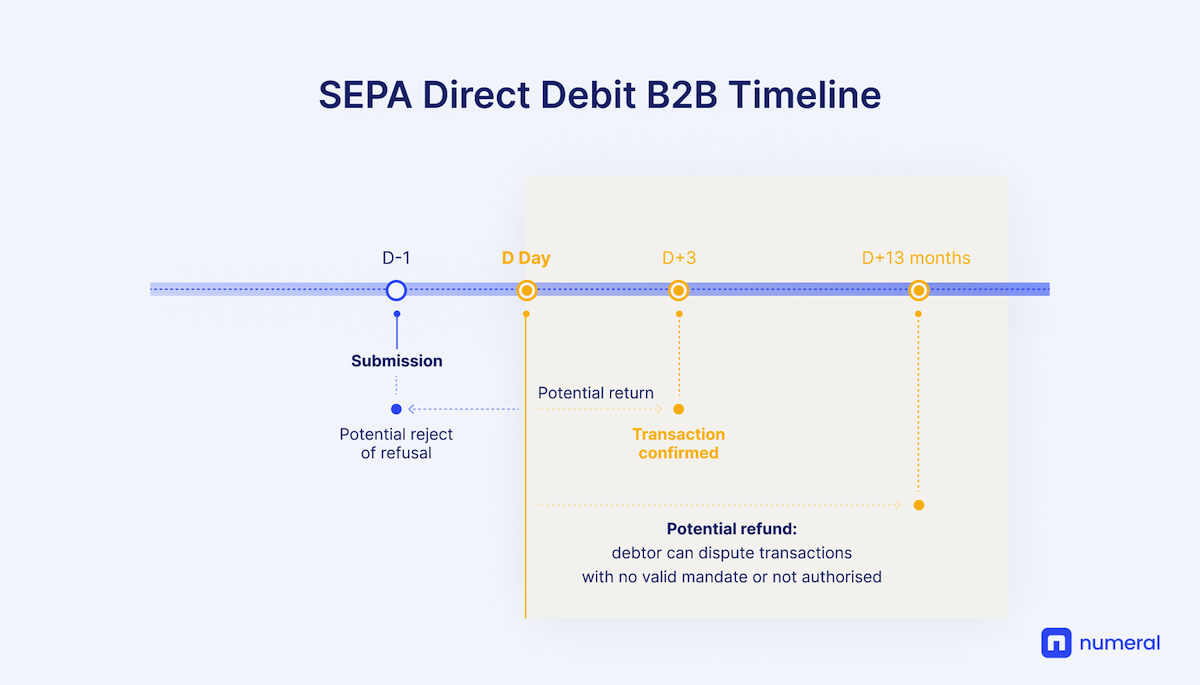
SEPA Direct Debit B2B
SEPA direct debit B2B payments are used between companies and with tax authorities. Common use cases include repaying loans, paying taxes, or paying for large purchases.
A SEPA direct debit business-to-business payment (called SEPA Direct Debit B2B, shortened to SDD B2B) is similar to a SEPA Direct Debit Core (SDD), with two major differences relevant for businesses: mandate verification and refund period.
Before an SDD B2B payment can be processed the mandate agreed between the parties must be sent to and registered by the debtor’s PSP. The requirement to register a mandate with the PSP does not apply to SDD Core payments, which makes SDD B2B payments unique in this respect. Furthermore, the debtor’s PSP is responsible for verifying that a SEPA direct debit B2B corresponds to a valid mandate before executing the payment and debiting the debtor’s account.
As a result of this extra step and the security implied for the debtor, a SEPA direct debit B2B payment cannot be refunded by the payer if there was a valid mandate and if the mandate had been authorised, unlike a SEPA direct debit core payment.
A SDD B2B payment can still be refunded up to 13 months after execution if there was no valid mandate or if it was not authorised. The debtor’s PSP may still return the payment up to three days after the execution for technical reasons or because the debtor PSP is unable to accept the collection for other reasons, such as the account being closed, the customer being deceased, the account not accepting direct debit, or the debtor refusing the debit.
A SEPA direct debit B2B payment must also be initiated between two weeks and one business day before its due date. But unlike with a SEPA direct debit core payment, a pre-notification of the debtor is not required.
Advantages
How does SEPA direct debit payment work?
SEPA direct debit was introduced by the European Payments Council for a standardized payment infrastructure within the European Union so that payments can be processed fully automatically within the Eurozone. The prerequisite for this is the written confirmation of a SEPA mandate to the Creditor. In the online sector, this mandate is usually given via electronic means. Novalnet offers you the possibility of SEPA direct debits collected fully automatically from the respective accounts of your customers.
How do you protect yourself against chargebacks?
There are many reasons for a chargeback. As a merchant, it is important that you are protected against fraudsters and payment defaults. For this purpose, Novalnet offers you comprehensive risk management services with numerous fraud prevention modules, including integrated fraud checks during the payment process, credit checks, plausibility checks and database checks. For example, you can use credit checks to automatically block payment methods during checkout so that customers with a low credit score can only opt for certain, secure payment methods.
Dunning process and Receivables management
In case payments fail to come in completely, Novalnet takes care of it through automated debt collection procedures, so that you as a merchant receive your money reliably. Our procedures are designed for personalization and through this ensures a high success rate in the dunning of outstanding amounts. If a dunning procedure is unsuccessful, the matter can be automatically transferred to an external collection agency. This process is completely transparent so that you are always informed about all the dunning steps. There are no additional costs for our receivables management with the exception of legal dunning procedures and postal payment reminders.
Integrated Accounts receivable management
In order not to lose track of your customers’ transactions and payments, we provide you with a comprehensive system for accounts receivable management. This enables us to keep all customer-related activities such as cash receipts, chargebacks, outstanding payments, debt-collection procedures, etc. are always up-to-date and transparent. Our accounts receivable management can be easily connected to existing inventory management systems and has extensive export functionalities simplifying accounting activities. Further advantages are the automation of processes and real-time monitoring. This saves costs and minimizes the risk of errors.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Кто может получить банковский счет SEPA?
Для отправки переводов SEPA вам не нужен определенный тип банковского счета. Эти переводы доступны для вас, если у вас есть банковский счет в зоне SEPA и ваш банк является членом SEPA.
Если вы не уверены, является ли ваш банк членом SEPA, уточните в своем банке или обратитесь к реестру учреждений-участников SEPA.
Какие лимиты переводов SEPA?
Лимит кредитных переводов SEPA составляет 999.999.999,99 EUR.
Максимальная сумма, которую вы можете перевести в качестве мгновенного кредитного перевода SEPA, с июля 2020 года составляет 100.000 EUR.
Прямые дебеты SEPA не имеют лимита перевода.
Могу ли я отправлять SEPA перевод в нескольких валютах?
Вы можете осуществить SEPA-перевод в другой валюте, если ваша транзакция осуществляется внутри зоны SEPA и между учреждениями в зоне SEPA.
Однако перевод SEPA может быть осуществлен только в евро, что означает, что ваши средства будут конвертированы в евро одним из банков, обрабатывающих транзакцию, прежде чем они дойдут до получателя.
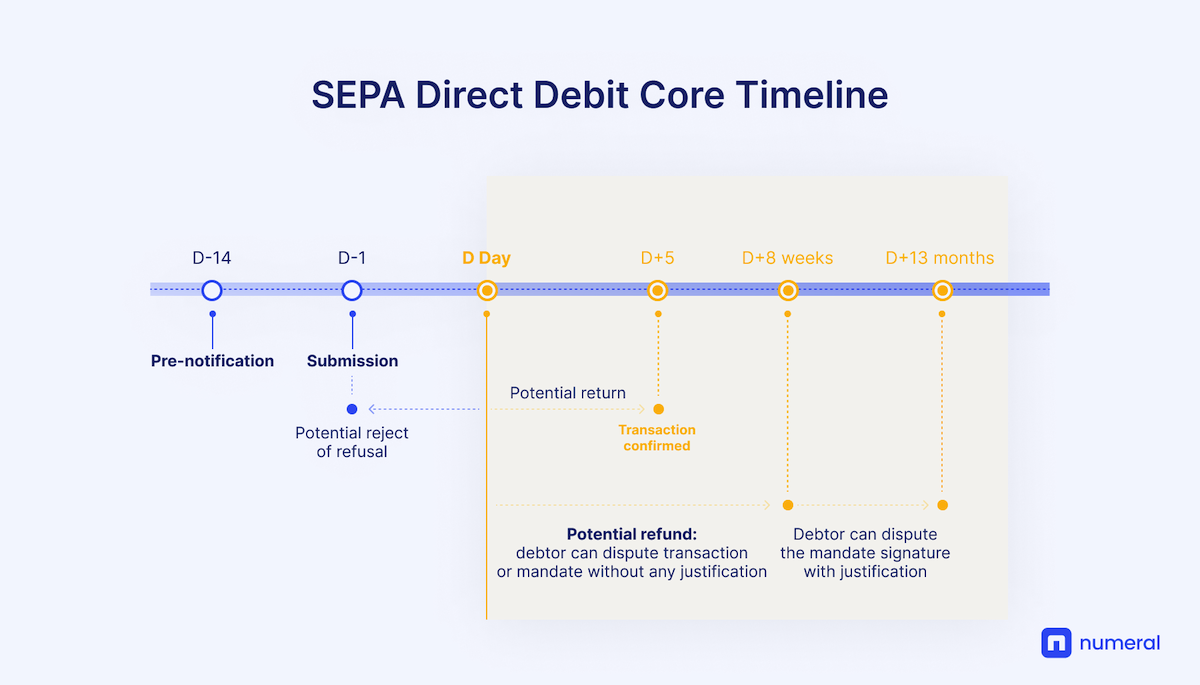
SEPA Direct Debit Core
A SEPA direct debit core (shortened to SDD core) is a payment pulled and debited from the debtor’s account and credited to the creditor’s account. SEPA direct debits are commonly used for recurring payments such as rent, utilities, software subscriptions, loan repayments, etc.
A SEPA direct debit core payment requires a mandate from the debtor to the creditor, which authorises the creditor to debit the debtor’s account under certain pre-agreed conditions.
The mandate is identified by a unique mandate reference (or UMR). The creditor is identified by a creditor identifier, which is usually assigned by the national bank of the country of the creditor.
The payment must be initiated between two weeks and two business days before its due date. It can be rejected by the debtor’s bank until five days after its due date, for instance if the account has been closed. The debtor needs to be notified two weeks in advance of the settlement date unless the debtor explicitly waives the notification.
A SEPA direct debit can be refunded up to eight weeks after execution. In that period, a refund can be requested even if there was a valid mandate and even if the payment had been authorised.
A refund can be then requested for up to 13 months after execution if there was no valid mandate, or if the payment was not authorised.
SEPA
Единая евро платежная зона SEPA – это инициатива Европейского Союза, направленная на упрощение банковских переводов в евро и объединения национальных рынков разных стран Европы в единый домашний рынок.
Страны зоны SEPA
SEPA охватывает весь Европейский Союз. Дополнительно, в нее входят и другие страны: Андорра, Исландия, Норвегия, Швейцария, Лихтенштейн, Монако, Сан-Марино, Великобритания, Ватикан, Майотта, Сен-Пьер и Микелон, Гернси, Джерси и остров Мэн.
Управление и координирование SEPA
SEPA координируется Европейской комиссией и Европейским центральным банком (ЕЦБ) через Европейский платежный совет. Совет возглавляет Европейский центральный банк, который вместе с представителями правительства и групп потребителей работает над управлением и повесткой дня.
Преимущества SEPA
• Единый рынок платежных услуг.• Упрощенная обработка платежей.• Снижение затрат на обработку платежей благодаря введению единых стандартов.• Снижение банковских комиссий за счет усиления конкуренции между игроками в зоне.• Сокращенное время обработки платежей
Виды SEPA переводов и SEPA схем
SEPA платежи делятся на разные виды переводов или платежных схем:
Кредитный перевод SEPA (SEPA Credit Transfer, SCT) позволяет переводить средства с одного банковского счета на другой. Это несрочный платеж в евро – дебетование счета в евро и зачисление на другой счет в евро в зоне SEPA. Схема кредитного перевода SEPA – это схема межбанковских платежей, которая гарантирует, что клиенты могут совершать электронные платежи любому клиенту, находящемуся в любой точке зоны SEPA, с использованием единого банковского счета (IBAN) и единого набора стандартов, правил и условий.
Мгновенный кредитный перевод SEPA (SEPA Instant Credit Transfer, SCT Inst) обеспечивает мгновенное зачисление средств с задержкой менее десяти секунд или максимум двадцать секунд в исключительных случаях.
Схема прямого дебетования SEPA (SEPA Direct Debit, SDD) позволяет производить платежи в евро как внутри страны, так и в других странах SEPA. Потребители могут оплачивать товары или услуги по всей Европе прямым дебетом так же легко, надежно и эффективно, как и в своей стране. Схема прямого дебетования SEPA позволяет автоматизировать транзакцию и не пропустить срок платежа.
What is the advantage of a SEPA Direct Debit over a standing order?
Compared to a standing order, the SEPA Direct Debit offers numerous advantages. Whereas with a standing order, the customer is responsible for making the payments on time, with the SEPA Direct Debit scheme the payee takes control of the payments.
The payee can automatically debit the amount from the customer’s account, reducing the workload for both parties. It is also easier to adjust in the event of changes such as new amounts or due dates, as the payee arranges this himself.
This makes the SEPA Direct Debit the ideal payment option for recurring payments whose amounts can potentially change (e.g., phone bills, memberships, any subscriptions). In addition, the SEPA Direct Debit is more flexible and offers the possibility to make one-time payments (e.g., online shop purchases).
Main differences between SEPA Core and B2B direct debits
| SEPA Core Direct Debit | SEPA B2B Direct Debit | |
| Debtor | The debtor may be a company or an individual. |
Both debtor and creditor must be companies.
This is a payment method reserved for professionals. |
| SEPA mandate | The debtor signs the direct debit mandate and sends it solely to the creditor. | The debtor signs two copies of the mandate and sends them to the creditor and his/her own bank (debtor’s bank). |
| Control of the mandate by the bank | The debtor’s bank does not need to have a copy of the mandate, and is not obliged to check its validity. | The debtor’s bank is aware of the mandate and verifies its validity. |
| Disputes and refunds |
The debtor may contest an authorized direct debit within 8 weeks of the date of execution. However, their claim for reimbursement is not fully guaranteed.
The debtor can contest an unauthorized direct debit within 13 months of the date of execution. However, their claim for reimbursement is not fully guaranteed. |
No refunds are possible after the authorized direct debit has been executed.
The debtor can contest an unauthorized direct debit within 13 months of the date of execution. However, their claim for reimbursement is not fully guaranteed. |
Focus on the SEPA creditor identifier, or SCI
The SEPA Creditor Identifier (SCI) is a unique, mandatory creditor reference that must appear on the direct debit mandate.
The SCI is structured in 4 parts, and its length varies from country to country, not exceeding 35 characters. It comprises the following elements:
- the country’s two-letter ISO code (FR for France);
- two control numbers;
- the 3-letter activity code;
- the national identifier. This is the NNE (Numéro National d’Émetteur), which has 13 characters in France.
What is a SEPA Transfer?
A SEPA transfer is an international transfer made through the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA), a European Union (EU) initiative for harmonising payments across Europe. The goal is to simplify cross-border money transfers in Euros. In several ways, a SEPA transfer is similar to a domestic transfer (or BACS transfer in the UK), as the banks that support SEPA payments either have direct relationships with other banks or a network of intermediary banks, enabling seamless transfers across international borders.
Within SEPA transfers, the European Payments Council (EPC) has created different SEPA payment schemes to match the various needs of people looking to use the network. These are SEPA Direct Debit (which includes both a ‘core’ and a ‘B2B’ service) and SEPA Credit Transfer.
The countries within SEPA are:
| Austria | Latvia |
| Belgium | Lichtenstein |
| Bulgaria | Lithuania |
| Croatia | Luxembourg |
| Cyprus | Malta |
| Czech Republic | Monaco |
| Denmark | Netherlands |
| Estonia | Norway |
| Finland | Poland |
| France | Portugal |
| Germany | Romania |
| Gibraltar | San Marino |
| Greece | Slovakia |
| Hungary | Slovenia |
| Iceland | Spain |
| Ireland | Sweden |
| Italy | Switzerland |
FAQs
Note
The order can change status several times, as the SEPA Direct Debit may be accepted by Cleverbridge only to be rejected later by the customer’s credit institution. For example, with a SEPA Direct Debit mandate provided with the initial order, the subscription renews successfully and the order status converts to Paid. Once the customer cancels the SEPA Direct Debit mandate and a return debit is successfully processed, the order status converts to Return Debit Waiting for Payment, only to revert back to Paid once the customer executes the payment via wire transfer.
How does Cleverbridge refund a return debit order?
An order paid by SEPA Direct Debit can be refunded following one of the two scenarios:
- Refund processed before Cleverbridge receives payment. The SEPA Direct Debit is canceled and the customer’s account is not debited.
- Refund processed after Cleverbridge receives payment. The debited amount will take up to four business days to be re-credited to the customer’s account.
Виды SEPA-переводов
В системе доступны несколько видов международных переводов:
Обычный платёж (SEPA Credit Transfer)
Это разовый перевод денег между банковскими счетами в разных странах ЕС. Для него используется идентификационный код IBAN. Такие платежи чаще всего применяют для единоразовой оплаты товаров и услуг. Если отправить перевод до конца рабочего дня, получатель заберёт деньги в тот же день.
Регулярный платёж (SEPA Direct Debit)
Это автоматические переводы между ЕС. Их можно настроить на фиксированное количество платежей. Такие переводы удобны для оплаты поставок, коммунальных услуг, взносов по кредитам.
Мгновенный платёж (SEPA Instant Credit Transfer)
Этот вид перевода для моментального списания и зачисления средств. Все операции проходят за секунды. Однако не все банки и даже страны подключены к «мгновенной» SEPA.
Кто может пользоваться SEPA
Воспользоваться услугами платёжной системы могут граждане и организации следующих 36 европейских стран:
- 27 государств-членов Европейского Союза (ЕС);
- 3 страны Европейской экономической зоны (Исландия, Лихтенштейн и Норвегия);
- 6 дополнительных европейских стран, не входящих в ЕЭЗ, но присоединившихся к SEPA (Швейцария, Монако, Сан-Марино, Андорра, Ватикан и Великобритания).
SEPA удобна для любых трансграничных переводов внутри Еврозоны. Ею пользуются частные лица, студенты, туристы, мигранты, а также компании, ведущие бизнес на территории ЕС. Например, если вы работаете в Швейцарии и открыли там счёт, то можете совершать мгновенные платежи в евро в любую страну Евросоюза. То же самое касается и компаний, ведущих бизнес на территории еврозоны.
Но, как вы понимаете, прямые платежи из России через SEPA совершать нельзя, поскольку она не входит в Европейское экономическое сообщество. Однако SEPA может быть полезна россиянам, у которых есть вид на жительство или официальная работа в европейских странах. Например, Великобритания, Болгария, Кипр, Италия и Португалия — популярные направления для эмиграции или открытия бизнеса. Если у вас есть ВНЖ в одной из этих стран, то можете открыть местный банковский счет. Это позволит пользоваться SEPA.
Если у вас уже есть европейская банковская карта, то вы получаете доступ к выгодным трансграничным переводам. Например, вы можете легко и дёшево отправить деньги родственникам в Россию. В этом вам поможет Monetory — покупаете USDT за евро через SEPA-перевод, а затем продаёте USDT уже в России – на банковскую карту или электронный кошелёк.
Попробовать!
How Does SEPA Direct Debit Work?
SEPA transfers work similarly to domestic transfers, with a few minor differences happening behind the scenes. Here’s how they work from the merchant’s perspective:
- Mandate
- Pre-notification
- Payment request
- Post-submission
Step 1: Mandate
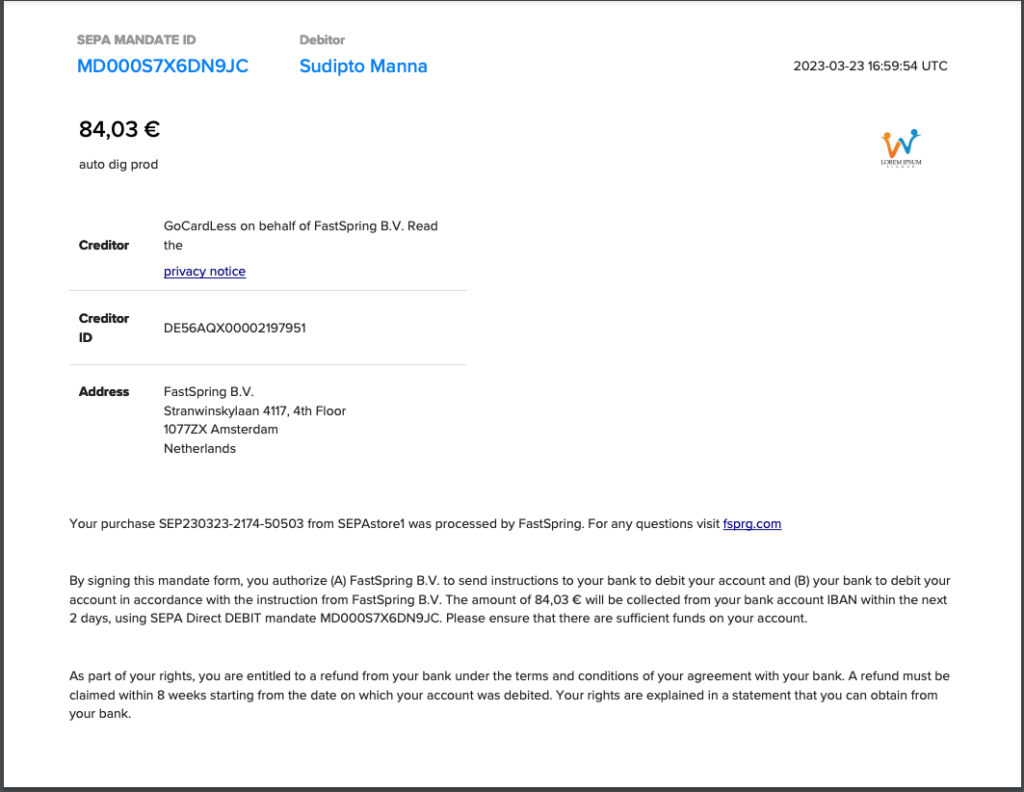
Before you can collect payment by SEPA Direct Debit, your customer must complete a mandate authorizing you to take payments. A mandate is the billing agreement given by a buyer to allow a seller to collect future payments from them from their Euro-denominated bank account.
Mandates must include certain mandatory information.
Required Items on a Mandate:
- Payment amount
- SEPA Mandate ID
- SEPA Mandate Date
- Merchant company name
- Merchant’s Creditor Identifier
- Merchant’s full address
- Creditor Information
- Type of payment
- International Bank Account Number (IBAN)
- Bank Identifier Code (BIC)
- Signed Date
- Signature
Here’s an example of FastSpring’s SEPA Mandate:
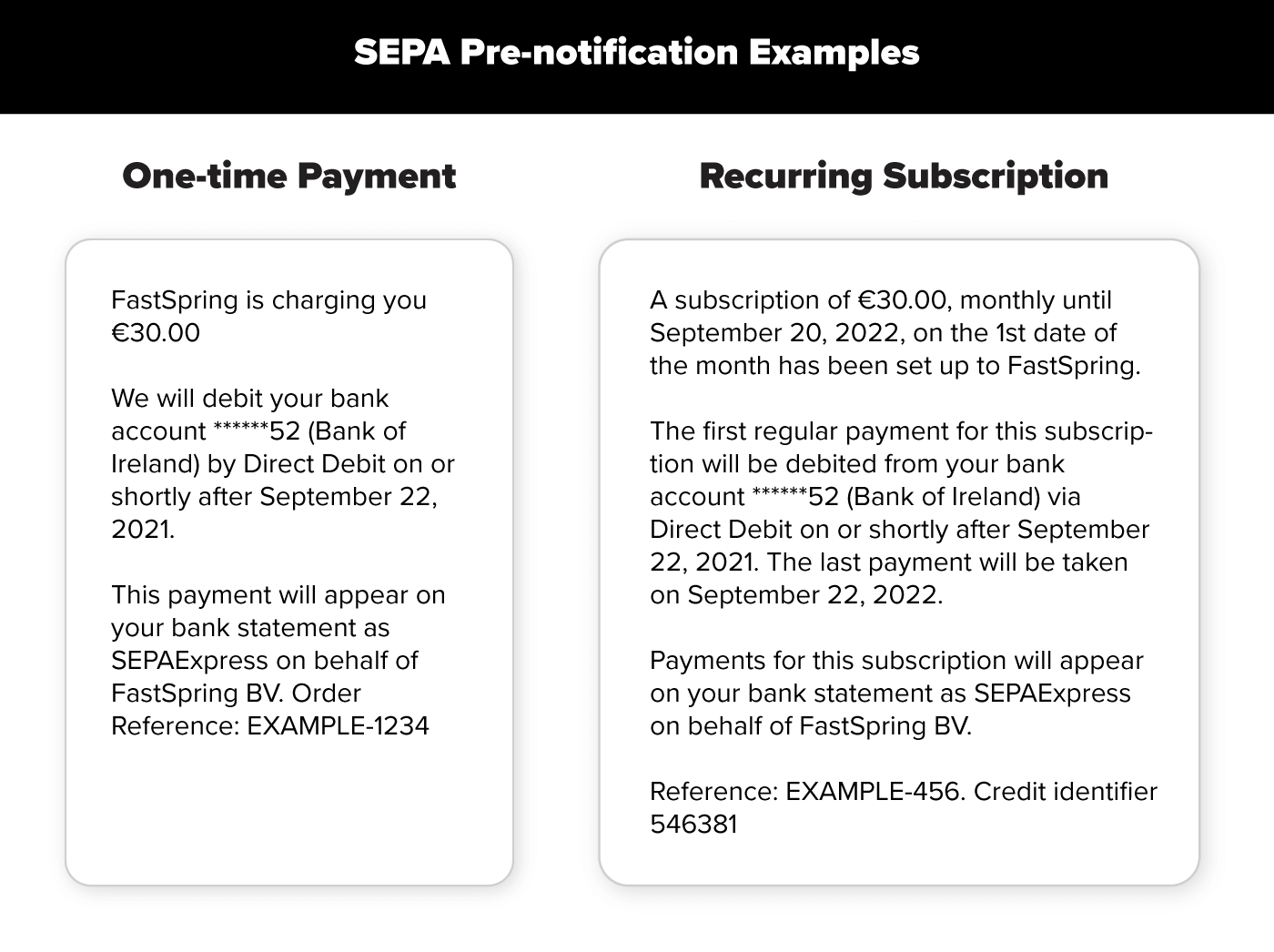
Step 2: Pre-Notification
Fully compliant pre-notifications require the following:
- Appropriate notice period (typically 14 calendar days)
- Amount, due date, mandate reference, and creditor ID
- Merchant’s contact information
Step 3: Payment Request
After the pre-notification is delivered, you can initiate payment by submitting the mandate-related data to the merchant’s bank. FastSpring does this step automatically for its sellers. The bank then forwards the request to the clearing and settlement mechanism, which will then forward this to the customer’s bank for settlement.
Step 4: Post-Submission
After you submit a payment, it will take 2-3 business days to know if a SEPA payment has succeeded or failed. That’s why we recommend waiting at least 48 hours to fulfill an order.
How SEPA direct debits work
The SEPA direct debit is an interbank transaction and a payment method controlled by the creditor.
Setting up SEPA SDD Core direct debits
To transfer funds from the debtor’s account to the creditor’s account and carry out a SEPA SDD Core Direct Debit, several steps are required.
- The creditor (or beneficiary) sends a direct debit mandate to the debtor (or payer).
- The latter fills in his or her contact details, IBAN and BIC code. They sign it and return it to the creditor, who keeps it in a safe place.
- 14 calendar days before the direct debit due date, and unless otherwise agreed bilaterally, the creditor informs the debtor of the date and amount of the transaction. The creditor issues the direct debit order to his or her bank, which forwards it to the debtor’s bank.
- The transaction is finalized by debiting the debtor’s account and crediting the creditor’s account.
Setting up SEPA SDD B2B direct debits
To transfer funds from the debtor’s account to the creditor’s account and carry out a SEPA SDD B2B direct debit, several steps are required.
- The creditor (or beneficiary) sends a direct debit mandate to the debtor (or payer).
- The debtor enters his or her contact details, IBAN and BIC code. The debtor signs two copies of the mandate and sends them to the creditor and their own bank (the debtor’s bank).
- 14 calendar days before the direct debit due date, the creditor informs the debtor of the date and amount of the transaction, as well as the UMR and SCI. The creditor issues the direct debit order to his or her bank, which forwards it to the CSM the day before the due date, and then to the debtor’s bank.
- The transaction is finalized by debiting the debtor’s account and crediting the creditor’s account.
Period of validity of the SEPA direct debit mandate
The period of validity of a SEPA direct debit mandate depends on the information indicated in the mandate. The mandate may be
- only valid for a single direct debit;
- or recurring, in which case it ends when the debtor revokes the agreement.
However, if no direct debit order is presented for 36 months, the mandate lapses.
Cancelling a SEPA direct debit
The debtor is entitled to claim repayment of the sums debited from his bank under certain conditions.
- Authorized SEPA Direct Debit (e.g. for the wrong amount): the customer has 8 weeks from the debit date to submit a request for reimbursement in the case of a SEPA Core Direct Debit. Please note: as mentioned above, it is not possible to dispute an authorized SEPA SDD B2B direct debit.
- Unauthorized or erroneous SEPA direct debit (invalidity or absence of mandate): the debtor has 13 months to contact their bank and provide the supporting documents needed to process the request for reimbursement.
What Is SEPA Direct Debit?
SEPA Direct Debit is an international wire transfer that allows merchants to collect payments from accounts in the countries and associated territories in the Single European Payments Area (SEPA).
SEPA is similar to ACH Debit (US) and EFT (Canada), except with a few notable differences:
| Currency | All SEPA Direct Debit transactions happen in Euros |
| Chargebacks | Buyers have 13 months to get a refund for unauthorized SEPA payments |
| Bank details | To collect SEPA payments, you need a customer’s IBAN |
| Implementation | Payment timing, how mandates are stored, and the submission process |
The European Payments Council launched SEPA to simplify cross-border transactions in Europe. The goal is to make global payments as easy and cheap as domestic payments by bringing together countries to create a single market for Euro-denominated transactions.
Why Is It So Important to Accept SEPA?
Today, more than 529 million citizens use SEPA to make over 146 billion electronic payments per year in the 36 member countries. This accounts for over 30% of online checkout in Europe, making it an important payment method to support if you’re selling into the European market.
European-Economic Area (EEA) SEPA Countries
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
Non-EEA SEPA Countries and Territories
- Andorra
- Monaco
- San Marino
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom
- Vatican City State
- Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon
- Guernsey
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
Additionally, any European with a bank account can pay with SEPA. By supporting this single payment option at checkout, you can reach over 500 million potential buyers across 36 countries.
The above list includes all countries in the SEPA region. For a list of countries FastSpring supports, please see our documentation.
To see more updates about how FastSpring supports SEPA transactions, view our more recent SEPA announcement here.
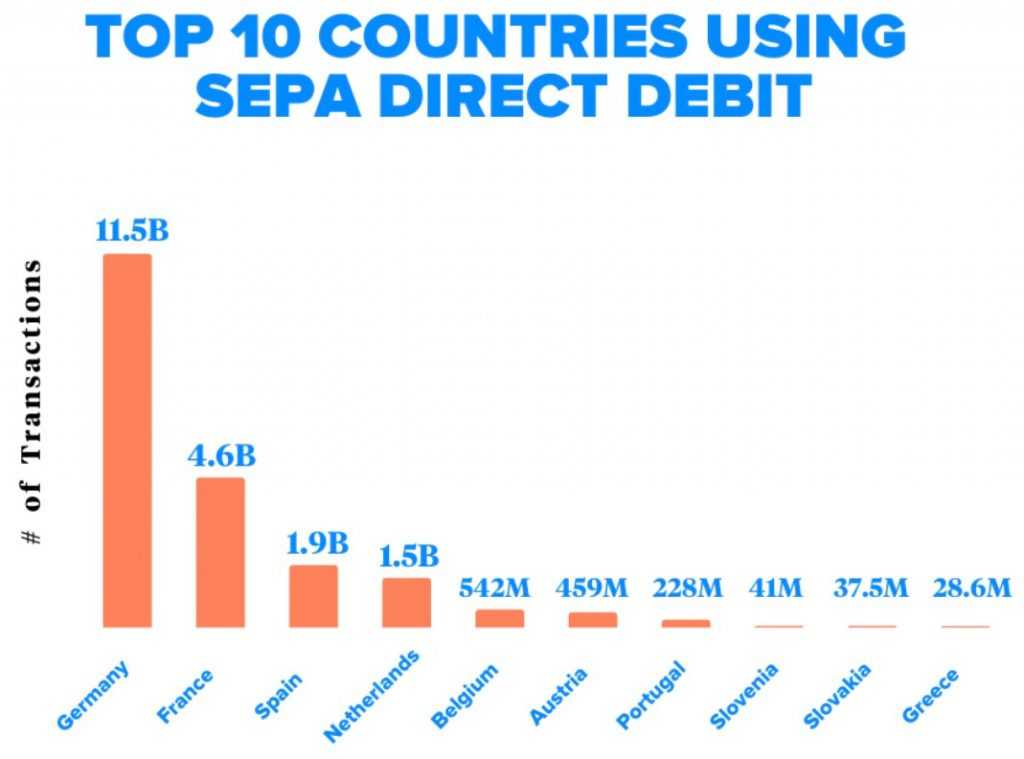
SEPA risks
SEPA Direct Debit scheme does not guarantee funds as your customer or their bank can initiate disputes.
- Any disputes raised by your customer with their bank within 8 weeks of the transactions will be automatically honored in alignment with SEPA guidelines.
- All returns, including those for disputes and insufficient funds, may attract a return fee. The return fee is charged by your customer’s bank and is passed on to you. Some banks may refuse to honour electronic mandates, and return MD01.
- If you have opted for instant settlement, settled fund may be debited from your account in case the customer is found not to have sufficient funds. In this case, settled funds will be debited after 1-2 days after the transaction.
- Instant settled transaction may eventually fail to settle and may have two associated return fees. The first return fee will be for the initial debit attempt. If this fails due to customer having insufficient funds, the re-presentment is triggered. If the re-presentment fails as well, a second returns fee may be charged.
- The SEPA Direct Debit scheme allows for returns to be initiated on any transaction, including those that you may have previously refunded. The scheme does not recognise refunds as being associated with original transaction, and does permits disputes on the original transaction.
Differences between SDD Core and SDD B2B
The SEPA B2B Direct Debit is an optional payment scheme, used only to manage the collection of business-to-business payments. It does not apply to individuals or auto-entrepreneurs. In contrast to the SDD Core Direct Debit, which applies to all payers and is mandatory for banks in the SEPA zone.
The SDD B2B is quicker to process and collect and has very restrictive refund conditions. B2B Direct Debit is a so-called “authorised” payment, so it is impossible to request a refund, except in cases of fraudulent or erroneous direct debits.
Treezor offers all SEPA payment solutions directly via API and can handle, within the Euro zone, the entire collection process on behalf of a company.
Declined transactions
If a direct debit is declined, a reason code is provided.
If the IBAN or BIC is incorrect, our bank informs us the next business day.
Reason codes and recommended responses
| Code | Reason | Recommended response |
|---|---|---|
| AC01 | Incorrect account number | Contact the debtor to confirm the IBAN. If there is a mandate amendment, check the data provided by the debtor. |
| AC04 | Closed account number | Contact the debtor to confirm the new IBAN. |
| AC06 | Blocked account | Contact the debtor for another account or means of payment. |
| AC13 | Debtor account type is missing or invalid | Contact the debtor for clarification and to agree another means of payment. |
| AG01 | Transaction forbidden | Contact the debtor for another account or means of payment. |
| AG02 | Invalid bank operation code | Resubmit the transaction with the correct authorization reference and transaction type: or . |
| AM04 | Insufficient funds | Contact the debtor to add funds to their account. |
| AM05 | Duplication | Contact your bank to confirm whether collection was duplicated. |
| BE04 | Creditor address missing or incorrect | |
| BE05 | Unrecognised initiating party | The creditor ID was incorrect or was changed without an amendment indicator. Check your contract for the correct creditor ID. If in doubt, contact your bank first. |
| CNOR | Creditor bank is not registered | Contact your bank. |
| DNOR | Debtor bank is not registered | Contact your bank. Contact the debtor for another means of payment. |
| ED05 | Settlement failed | Depends on the SLA between the debtor’s bank and the Clearing and Settlement Mechanism (CSM). |
| FF01 | Invalid file format | Repair the XML file. |
| FF05 | Direct debit type incorrect | |
| FOCR | Return following a cancellation request | |
| MD01 | No mandate | Analyse the characteristics of the SDD collection. Contact the debtor if they request a refund. |
| MD02 | Required infomation missing from mandate | Amend the mandate. |
| MD06 | Customer requested chargeback | Contact the debtor. |
| MD07 | Customer deceased | Close the agreement with the deceased debtor. |
| MS02 | Unspecified reason generated by customer | Contact the debtor. |
| MS03 | Unspecified reason generated by agent | Contact the debtor. |
| RC01 | Incorrect bank identifier | Contact the debtor for the correct BIC for a non-EEA collection. Ask your bank to allocate the debtor’s bank’s correct BIC in the interbank message. |
| RR01 | Missing debtor account or identification | Repair the collection to complete the debtor’s account information. Contact your bank. |
| RR02 | Missing debtor name or address | Repair the collection to complete the debtor’s name and/or address. Contact your bank.Note: To avoid declined transactions, non-EEA countries must include name and address in the . |
| RR03 | Missing creditor name or address | Repair the collection to complete your name. Contact your bank. |
| RR04 | Regulatory reason | Contact your bank. |
| SL01 | Specific service offered by debtor agent | Contact the debtor. |
| TM01 | File received after cut-off time |
For more information in:
- English, see European Payments Council – Guidance on reason codes .
- Dutch, see Betaal Vereniging – Reasoncodes en vervolgacties .



























